An internal combustion engine that can run on two different fuels concurrently or alternately is referred to as a dual fuel engine or a bi-fuel engine. Using a primary fuel, usually diesel or natural gas, and a secondary fuel, frequently gaseous fuels like propane, methane, or hydrogen, is the most popular dual fuel engine arrangement. Depending on the engine design, the simultaneous or sequential ignition of the two fuels takes place throughout the combustion process in a dual fuel engine.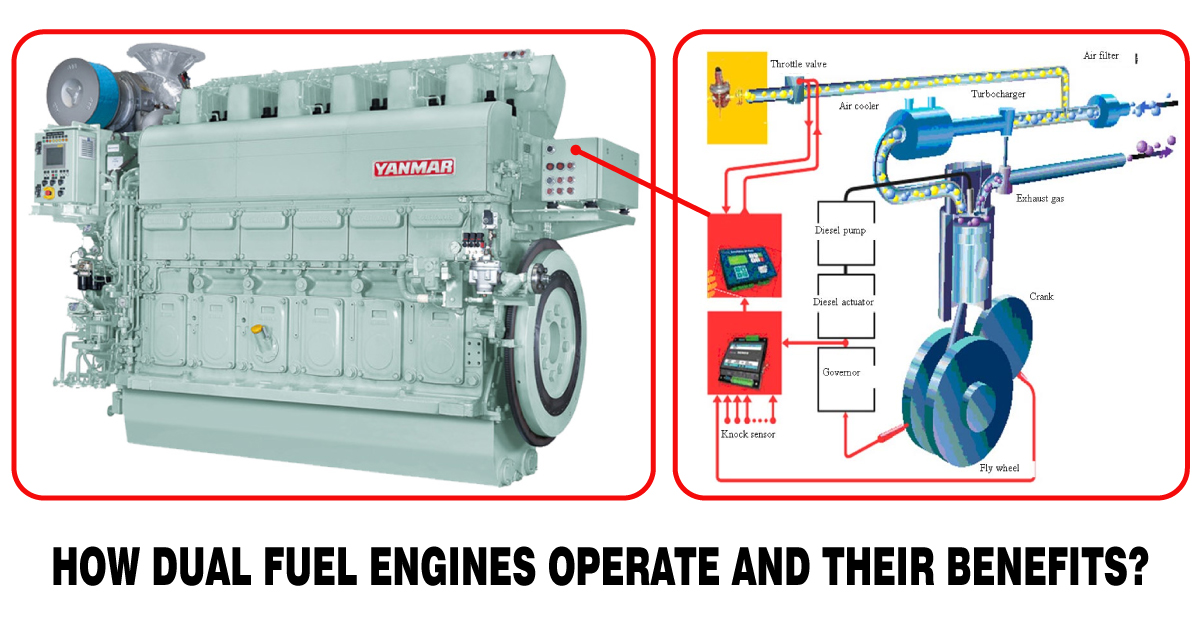
Here is a brief explanation of how a dual fuel engine usually operates:
- Fuel Injection: Using conventional direct injection techniques, the primary fuel—typically diesel—is injected into the combustion chamber. The engine’s ignition is provided by this fuel.
- Secondary Fuel Injection: Gaseous secondary fuel, such natural gas, is injected into the combustion chamber or intake manifold. Usually, it is blended with air before being injected into the engine.
- Ignition: Similar to a traditional diesel engine, the primary fuel (diesel) is ignited during the compression stroke of the engine. The heat and pressure required to ignite the secondary fuel are produced by this high-temperature combustion process.
- Dual Combustion: The primary fuel’s combustion produces high temperatures and pressure, which cause the secondary fuel to ignite when it is combined with air. The engine receives its power from this dual combustion process.
Benefits of dual-fuel engines:
- Efficiency: When compared to conventional single-fuel engines, dual fuel engines can provide better thermal efficiency and fuel economy. Gaseous fuels can enhance overall engine efficiency and cut back on pollutants.
- pollutants Reduction: When compared to diesel fuel, gaseous fuels like natural gas emit less hazardous pollutants (such NOx and particulate matter). Due of this, dual fuel engines are a desirable alternative for adhering to more stringent pollution laws.
- Fuel Flexibility: Dual fuel engines enable for the use of a variety of fuels, giving operators the freedom to select the most affordable or accessible fuel source. This can be especially helpful in areas with fluctuating gasoline prices.
- Extended Engine Life: Longer Maintenance Intervals and lower Engine Wear, the cleaner combustion of gaseous fuels may result in longer maintenance intervals and lower engine wear, thereby prolonging the engine’s useful life.
- Reduced Noise: Due to their propensity to run more quietly than conventional diesel engines, dual fuel engines are appropriate for situations where noise pollution is an issue.
- Reduced Knocking: Compared to diesel, gaseous fuels offer greater octane ratings, which lower knocking and permit higher compression ratios, potentially improving engine performance.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Using gaseous fuels may dramatically lower an engine’s carbon footprint, especially if they are generated from sustainable sources like biogas or hydrogen.
It’s important to keep in mind that a dual fuel engine’s specific benefits might change according on the application, the fuels utilized, and the engine’s design. Although they have many advantages, they also have drawbacks, such as the necessity for specialized fuel storage and injection systems and the difficulty of controlling dual fuels during combustion. The unique needs and objectives of the application should be taken into consideration while selecting a dual fuel engine.
 widemep.com
widemep.com